In Tableau, you can aggregate measures or dimensions, though it is more common to aggregate measures. Whenever you add a measure to your view, an aggregation is applied to that measure by default. The type of aggregation applied varies depending on the context of the view.
- How To Remove Avg Toolbar
- Avg Safe Search Toolbar
- Avg Toolbar Download
- Avg Toolbar Install
- Avg Toolbar Free
- What Is Avg Safeguard Toolbar
- What Is Avg Nation Toolbar Free
Watch a Video: To see related concepts demonstrated in Tableau, watch Aggregation, Granularity, and Ratio Calculations(Link opens in a new window), a 4-minute free training video. Use your tableau.com(Link opens in a new window) account to sign in.
Change the Aggregation of a Measure in the View
When you add a measure to the view, Tableau automatically aggregates its values. Sum, average, and median are common aggregations; for a complete list, see List of Predefined Aggregations in Tableau.
The current aggregation appears as part of the measure's name in the view. For example, Sales becomes SUM(Sales). Every measure has a default aggregation which is set by Tableau when you connect to a data source. You can view or change the default aggregation for a measure—see Set the Default Aggregation for a Measure.
You can aggregate measures using Tableau only for relational data sources. Multidimensional data sources contain data that is already aggregated. In Tableau, multidimensional data sources are supported only in Windows.
You can change the aggregation for a measure in the view from its context menu:
Aggregating Dimensions
Ask.com is the #1 question answering service that delivers the best answers from the web and real people - all in one place. AVG Nation search & AVG Nation Toolbar are installed on your computer when you install AVG Link Scanner from AVG Technologies. The AVG Nation search settings offer browser safety and security features when you browse the Internet.
You can aggregate a dimension in the view as Minimum, Maximum, Count, or Count (Distinct). When you aggregate a dimension, you create a new temporary measure column, so the dimension actually takes on the characteristics of a measure.
Note: The Count (Distinct) aggregation is not supported for Microsoft Access data sources, and for Microsoft Excel and Text File data sources using the legacy connection. If you are connected to one of these types of data sources, the Count (Distinct) aggregation is unavailable and shows the remark 'Requires extract.' If you save the data source as an extract, you will be able to use the Count (Distinct) aggregation.
Another way to view a dimension is to treat it as an Attribute. Do this by choosing Attribute from the context menu for the dimension. The Attribute aggregation has several uses:
It can ensure a consistent level of detail when blending multiple data sources.
It can provide a way to aggregate dimensions when computing table calculations, which require an aggregate expression.
It can improve query performance because it is computed locally.
Tableau computes Attribute using the following formula:
IF MIN([dimension]) = MAX([dimension]) THEN MIN([dimension]) ELSE '*' END
The formula is computed in Tableau after the data is retrieved from the initial query. The asterisk (*) is actually a visual indicator of a special type of Null value that occurs when there are multiple values. See Troubleshoot Data Blending(Link opens in a new window) to learn more about the asterisk.
Below is an example of using Attribute in a table calculation. The table shows sales by market, market size, and state. Suppose you wanted to compute the percent of total sales each state contributed to the market. When you add a Percent of Total quick table calc (see Quick Table Calculations(Link opens in a new window)) that computes along State, the calculation computes within the red area shown below. This is because the Market Size dimension is partitioning the data.
How To Remove Avg Toolbar
When you aggregate Market Size as an Attribute, the calculation is computed within the Market (East, in the following image), and the Market Size information is used purely as a label in the display.
List of Predefined Aggregations in Tableau
Sometimes it is useful to look at numerical data in an aggregated form such as a summation or an average. The mathematical functions that produce aggregated data are called aggregation functions. Aggregation functions perform a calculation on a set of values and return a single value. For example, a measure that contains the values 1, 2, 3, 3, 4 aggregated as a sum returns a single value: 13. Or if you have 3,000 sales transactions from 50 products in your data source, you might want to view the sum of sales for each product, so that you can decide which products have the highest revenue.
You can use Tableau to set an aggregation only for measures in relational data sources. Multidimensional data sources contain aggregated data only.
Note: Using floating-point values in combination with aggregations can sometimes lead to unexpected results. For details, see Understanding data types in calculations(Link opens in a new window).
Tableau provides a set of predefined aggregations that are shown in the table below. You can set the default aggregation for any measure that is not a calculated field that itself contains an aggregation, such asAVG([Discount]). See Set the Default Aggregation for a Measure. You can also set the aggregation for a field already in the view. For details, see Change the Aggregation of a Measure in the View. | Aggregation | Description | Result for measure that contains 1, 2, 2, 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Attribute | Returns the value of the given expression if it only has a single value for all rows in the group, otherwise it displays an asterisk (*) character. Null values are ignored. This aggregation is particularly useful when aggregating a dimension. To set a measure in the view to this aggregation, right-click (control-click on Mac) the measure and choose Attribute. The field then changes to show the text ATTR: | N/A |
| Dimension | Returns all unique values in a measure or dimension. | 3 values (1, 2, 3) |
| Sum | Returns the sum of the numbers in a measure. Null values are ignored. | 1 value (8) |
| Average | Returns the arithmetic mean of the numbers in a measure. Null values are ignored. | 1 value (4) |
| Count (Distinct) | Returns the number of unique values in a measure or dimension. When applied to a dimension, Tableau creates a new temporary column that is a measure because the result of a count is a number. You can count numbers, dates, booleans, and strings. Null values are ignored in all cases. This aggregation is not available for the following types of workbooks:
If you are connected to a workbook that uses of one of these types, Count (Distinct) is unavailable and Tableau shows the message 'Requires extract.' To use this aggregation, extract your data. See Extract Your Data. | 1 value (3) |
| Minimum | Returns the smallest number in a measure or continuous dimension. Null values are ignored. | 1 value (1) |
| Maximum | Returns the largest number in a measure or in the given expression based on a sample population. Null values are ignored. Returns a Null if there are fewer than 2 members in the sample that are not Null. Use this function if your data represents a sample of the population. | 1 value (3) |
| Std. Dev (Pop.) | Returns the standard deviation of all values in the given expression based on a biased population. Assumes that its arguments consist of the entire population. Use this function for large sample sizes. | 1 value (0.7071) |
| Variance | Returns the variance of all values in the given expression based on a sample. Null values are ignored. Returns a Null if there are fewer than 2 members in the sample that are not Null. Use this function if your data represents a sample of the population. | 1 value (0.6667) |
| Variance (Pop.) | Returns the variance of all values in the given expression based on a biased population. Assumes that its arguments consist of the entire population. Use this function for large sample sizes. | 1 value (0.5000) |
| Disaggregate | Returns all records in the underlying data source. To disaggregate all measures in the view, select Aggregate Measures from the Analysis menu (to clear the check mark). Tableau allows you to view data in disaggregated form (relational databases only). When data are disaggregated, you can view all of the individual rows of your data source. For example, after discovering that the sum of sales for rubber bands is $14,600, you might want to see the distribution of individual sales transactions. To answer this question, you need to create a view that shows individual rows of data. That is, you need to disaggregate the data (see How to Disaggregate Data). Another way to look at disaggregated data is to view the underlying data for all or part of a view. For more details, see View Underlying Data. | 4 values (1, 2, 2, 3) |
You can also define custom aggregations as described in Aggregate Functions in Tableau(Link opens in a new window). Depending on the type of data view you create, Tableau will apply these aggregations at the appropriate level of detail. For example, Tableau will apply the aggregation to individual dimension members (the average delivery time in the East region), all members in a given dimension (the average delivery time in the East, West, and Central regions), or groups of dimensions (the sum of sales for all regions and for all markets).
Set the Default Aggregation for a Measure
You can set the default aggregation for any measure that is not a calculated field that itself contains an aggregation, such as AVG([Discount]). A default aggregation is a preferred calculation for summarizing a continuous or discrete field. The default aggregation is automatically used when you drag a measure to a view.
To change the default aggregation:
Right-click (control-click on Mac) a measure in the Data pane and select Default Properties > Aggregation, and then select one of the aggregation options.
Note: You can use Tableau to aggregate measures only with relational data sources. Multidimensional data sources contain aggregated data only.
You cannot set default aggregations for published data sources. The default aggregation is set when the data source is initially published. Create a Local Copy(Link opens in a new window) of the published data source to adjust the default aggregation.
How to Disaggregate Data
Whenever you add a measure to your view, an aggregation is applied to that measure by default. This default is controlled by the Aggregate Measures setting in the Analysis menu.
If you decide you want to see all of the marks in the view at the most detailed level of granularity, you can disaggregate the view. Disaggregating your data means that Tableau will display a separate mark for every data value in every row of your data source.
To disaggregate all measures in the view:
Clear the Analysis >Aggregate Measures option. If it is already selected, click Aggregate Measures once to deselect it.
When Aggregate Measures is selected, Tableau will attempt to aggregate measures in the view by default. This means that it collects individual row values from your data source into a single value (which becomes a single mark) adjusted to the level of detail in your view.
The different aggregations available for a measure determine how the individual values are collected: they can be added (SUM), averaged (AVG), or set to the maximum (MAX) or minimum (MIN) value from the individual row values.
For a complete list of the available aggregations, List of Predefined Aggregations in Tableau.
The level of detail is determined by the dimensions in your view—for information about the concept of level of detail, see How dimensions affect the level of detail in the view.
Disaggregating your data can be useful for analyzing measures that you may want to use both independently and dependently in the view. For example, you may be analyzing the results from a product satisfaction survey with the Age of participants along one axis. You can aggregate the Age field to determine the average age of participants or disaggregate the data to determine at what age participants were most satisfied with the product.
Disaggregating data can be useful when you are viewing data as a scatter plot. See Example: Scatter Plots, Aggregation, and Granularity.
Note: If your data source is very large, disaggregating the data can result in a significant performance degradation.
Example: Scatter Plots, Aggregation, and Granularity
If you place one measure on the Rows shelf and another measure on the Columns shelf, you are asking Tableau to compare two numerical values. Typically, Tableau chooses a scatter plot as the default visualization in such cases. The initial view will most likely be single mark, showing the sum for all values for the two measures. This is because you need to increase the level of detail in the view.
Start building the scatter plot
There are various ways to add detail to a basic scatter plot: you can use dimensions to add detail, you can add additional measures and/or dimensions to the Rows and Columns shelves to create multiple one-mark scatter plots in the view, or you can disaggregate the data. And, you can also use any combination of these options. This topic looks at these alternatives using the Sample-Superstore data source.
To create the initial view, follow these steps:
Place the Sales measure on the Columns shelf.
Place the Profit measure on the Rows shelf.
The measures are automatically aggregated as sums. The default aggregation (SUM) is indicated in the field names. The values shown in the tooltip show the sum of sales and profit values across every row in the data source.
Follow the steps below to use dimensions to add detail to the view and to disaggregate data.
Use dimensions to add detail
Follow these steps to develop the scatter plot view you created above by adding dimensions to show additional levels of detail.

Drag the Category dimension to Color on the Marks card.
This separates the data into three marks—one for each dimension member—and encodes the marks using color.
Drag the State dimension to Detail on the Marks card.
Now there are many more marks in the view. The number of marks is equal to the number of distinct states in the data source multiplied by the number of categories.
Although more marks are now displayed, the measures are still aggregated. So regardless of whether there is one row in the data source where State = North Dakota and Category= Furniture, or 100 such rows, the result is always a single mark.
Maybe this process is developing the view in a direction you find useful, or maybe you prefer to go in a different direction—for example, by adding a time dimension to the view, or by introducing trend lines or forecasting. You decide what questions to ask.
Avg Safe Search Toolbar
Try adding more fields to the rows and columns shelves
Revert to the original one-mark view and follow these steps to develop the scatter plot view by adding fields to the Rows and Columns shelves.
Drag the State dimension to the Columns shelf.
Even if you drop Continent to the right of SUM(Sales), Tableau moves it to the left of SUM(Sales). This is because you cannot insert a dimension within a continuous axis. Instead, your view shows a separate axis for each member of the dimension.
Drag the Segment dimension to the Rows shelf.
You now have a view that provides an overview of Sales and Profit across states and customer segments. It can be interesting to hover over the marks in the view to see tooltip data for various segments:
Try disaggregating the data
Another way to modify your original one-mark scatter plot to display more marks is by disaggregating the data.
Clear the Analysis >Aggregate Measures option. If it is already selected, click Aggregate Measures once to deselect it.
What you have actual done is to dis-aggregate the data, because this command is a toggle that was originally selected (check mark present). Tableau aggregates data in your view by default.
Now you see a lot of marks—one for each row in your original data source:
When you disaggregate measures, you no longer are looking at the average or sum for the values in the rows in the data source. Instead, the view shows a mark for every row in the data source. Disaggregating data is a way to look at the entire surface area of the data. It's a quick way to understand the shape of your data and to identify outliers. In this case, the disaggregated data shows that for many rows in the data, there is a consistent relationship between sales income and profit—this is indicated by the line of marks aligned at a forty-five degree angle.
Nation Toolbar (also found as Nation Community Toolbar, AVG Nation Toolbar, Nation virus, Nation Search virus; though not technically a computer virus) is malware categorized as a browser hijacker that primarily bundles with third-party software without user consent and causes additional complications for computer users. Nation Toolbar downloads and installs to a Microsoft Windows computer systems and attaches to Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Microsoft Internet Explorer as a browser add-on, browser helper object (BHO), and extension. In turn, Nation Toolbar changes Microsoft Windows Operating System settings, as well as Internet Browser settings including the homepage, managed, provided, and default search engine; causing unwanted browser redirects to search.nation.com, avg.nation.com, nation.com, search.conduit.com, and other unwanted websites.
Once installed Nation malware begins to replace existing Windows and browser settings and will appear at the top of an open browser window. Nation Toolbar will also cause internet browsers to start up on search.nation.com and other unwanted websites when users open a new browser window or tab.
Nation Toolbar and associated third-party items may also be the culprit of unwanted advertisements, including pop-up advertisements, banner ads, in-text ads, and more. Removing Nation Toolbar and similar items often stops unwanted advertisements from appearing.
Nation Toolbar hijacker and similar forms of malware raise many concerns relating to the invasion of privacy and privacy crimes. If Nation Toolbar is installed, the add-on and extension, as well as third-party items may collect and distribute sensitive user information; especially information users manually submit online or to third-party software including full names, usernames, passwords, email addresses, telephone numbers, and home addresses.
Nation Toolbar even has permission to access all the data on your computer and the websites you visit. The information collected may be used to submit users to marketing and mailing lists without their direct consent or knowledge. Victims may receive unwanted email spam, junk mail, and telephone calls from telemarketers relative to recent internet browsing activities.
On a more severe scale, Nation Toolbar and similar browser hijacker malware infections put users at risk of cyber crimes including credit theft, extortion, and identity theft.
How does Nation Toolbar malware get onto a computer?
Nation.com malware primarily bundles with third-party downloadable content including freeware and shareware available from download.com and similar websites. During the installation process of third-party items users may be given the opportunity to accept or decline an offer to install Nation Toolbar and change internet browser settings including the homepage and default search engine to search.nation.com or search.conduit.com; However, the request to decline the offer is often ignored or represented in a confusing manner.
It is recommended to avoid questionable downloads from websites such as download.com as their primary objective is to aggressively generate revenue off the confusion of their users and visitors.
Nation Toolbar can also be contracted from various locations including advertisements, social media content, email spam, sponsored search results, and more.

- Automatically remove Nation Toolbar – Scan for and automatically remove Nation Toolbar and third-party malware
- Manually remove Nation Toolbar – Remove/Uninstall Nation Toolbar software and third-party malware (if necessary)
- For Tech Support – Call 1-888-986-8411 and they will kindly assist you with removing this infection
Use the instructions below to automatically remove Nation Toolbar and third-party malware, as well as automatically remove unwanted search engines from your installed internet browsers.
Malwarebytes Anti-Malware
Avg Toolbar Download
1. We highly recommend writing down the toll free number below in case you run into any issues or problems while following the instructions. Our techs will kindly assist you with any problems.
if you need help give us a call
2. Install the free or paid version of Malwarebytes Anti-Malware.
3. Once Malwarebytes is installed, run the program. If you are using the free version of Malwarebytes you will be prompted to update the database, make sure to do so.
4. On the first tab labeled “Scanner” select the Perform full scan option and click the Scan button to perform a full system scan. Malwarebytes will automatically detect malware infecting the computer system.
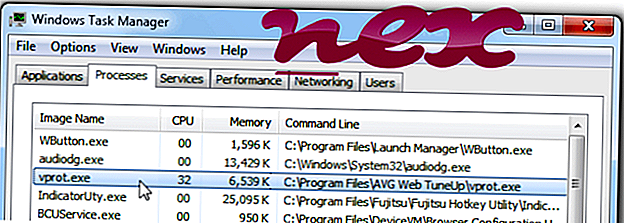
5. Once the malware scan is complete, Malwarebytes may prompt a notice stating malicious objects were detected. Select the malicious objects and click the Remove Selected button to completely remove the malicious files from your computer (the image below shows a file that is NOT selected) or click the Delete button to remove quarantined files.
CCleaner
CCleaner can be used to automatically repair internet browser settings startup up settings, and uninstall Nation malware and associated third-party software.
1. Install the free or paid version ofCCleaner by Piriform.
2. Once installed, open the program and navigate to Cleaner > Windows/Applications and click the Analyze button. Afterwards, click the Run Cleaner button on the bottom right of the program interface.
3. Next, navigate to Tools > Startup and search through each tab starting from windows, internet explorer, etc., all the way to Content Menu, for additional suspicious entries and click Disable and Delete once anything is found.
4. To automatically uninstall Nation Toolbar and other unwanted programs, navigate to the Uninstall tab and search for Nation Toolbar (nation, search protect by conduit, etc.) in the list of installed programs. Uninstall the unwanted software as selected by clicking the Run Uninstaller button.
Use the instructions below to manually uninstall Nation Toolbar malware and third-party software using Microsoft Windows removal procedures.
How to uninstall Nation Toolbar
1. Access Windows Start Menu and navigate to the Control Panel.
2. Click Uninstall a program or Add and remove a program.
3. In the list of installed programs search for Nation Toolbar and other potentially unwanted software. Once Nation Toolbar is located, double click the unwanted program(s) or highlight them in the list and click the Uninstall button.
How to remove Nation Toolbar add-ons and extensions
Use the instructions to remove Nation Toolbar add-ons, extensions, plug-ins, and additional toolbars. Please note, it may be necessary to remove multiple third-party items.
Google Chrome
1. Click on the Customize icon (wrench or 3 bar icon) next to the address bar and navigate to Tools > Extensions.
2. Search for the Nation Toolbar extension and remove it by clicking the trashcan icon next to them.
Mozilla Firefox
1. Type Ctrl+Shift+A.
2. On the Extensions and Plugin search for the Nation Toolbar add-on and remove it.
Microsoft Internet Explorer
1. Click Tools and select Manage add-ons.
2. On the Toolbars and Extensions tab search for the Nation Toolbar add-on and remove it if located.
How to remove search.nation.com Search Engine
Avg Toolbar Install
- In Mozilla Firefox, click the small search magnify glass near the search box (not url/search field) and click “Manage Search Engines…”. Remove the search.nation.com search engine from the list of search providers by highlighting the selections and clicking remove.
- In Microsoft Internet Explorer navigate to Tools > Manage Add Ons > Search Providers and remove the search.nation.com search engine from the list.
- In Google Chrome, click the customize icon (wrench or 3 bars) and navigate to Settings > Manage search engines… click the X next to the search.nation.com search engine to remove it.
Please note, If http://www.search.nation.com/ (etc.) is set as Google Chrome’s default search engine, add (or select) a new search engine (such as Google.com) and select the new search engine as the default search engine, then remove the unwanted search engine by clicking the X next to it.
How to remove search.nation.com from Homepage
Avg Toolbar Free
- In Mozilla Firefox navigate to Tools > Options or click Firefox in the top left corner and click Options > Options. Under the General tab remove search.nation.com from the “Home Page:” field and replace it with your preferred home page URL.
What Is Avg Safeguard Toolbar

What Is Avg Nation Toolbar Free
- In Microsoft Internet Explorer navigate to Tools >Internet Options. Remove search.nation.com from the Home Page field and replace it with your preferred URL.
- In Google Chrome click the customize icon (wrench or 3 bars) and navigate to Settings.Click “Set pages” under the On startup option. Remove search.nation.com and replace it with your preferred URL.



